
As waste volumes continue to rise globally, industries and municipalities are increasingly turning to thermal treatment technologies to process biomass and municipal solid waste (MSW) in a cleaner and more efficient way. Among the available options, pyrolysis and torrefaction are two widely discussed processes.
While both technologies involve heating waste materials in low-oxygen conditions, they serve different purposes and offer different advantages. This blog explains pyrolysis and torrefaction in simple terms, compares their key differences, and highlights why torrefaction is often the preferred solution, particularly when dealing with mixed waste streams like MSW.
Understanding Thermal Treatment of Biomass and MSW
Biomass and MSW contain significant energy potential, but their raw form poses challenges such as high moisture content, inconsistent composition, and poor fuel quality. Thermal processing helps address these issues by converting waste into more stable and usable products.
Both pyrolysis and torrefaction are used in biomass processing, MSW treatment, and waste-to-energy systems, but their outcomes and operational requirements vary significantly.
What Is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process in which biomass or MSW is heated at high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 700°C, in the absence of oxygen.
The objective of pyrolysis is to break down complex organic materials into multiple products:
- Solid char
- Liquid bio-oil
- Syngas
When applied to MSW, pyrolysis often requires extensive pre-treatment and sorting to manage non-combustible and heterogeneous waste components. The presence of plastics, inert materials, and contaminants can complicate process control and downstream handling.
Key Characteristics of Pyrolysis
- High operating temperatures
- Multiple output streams
- Complex system design
- Higher capital and operational costs
Pyrolysis is suitable when the goal is fuel diversification or chemical recovery, but it can be challenging for large-scale, mixed MSW processing.
What Is Torrefaction?
Torrefaction is a milder thermal treatment process that upgrades biomass and combustible fractions of MSW into a high-quality solid fuel. It typically operates at 250°C to 350°C in an oxygen-free environment.
During torrefaction:
- Moisture is removed
- Light volatiles are released
- The solid structure is retained
The result is torrefied biomass or torrefied MSW fuel, a coal-like product with improved energy density, better grindability, and enhanced storage stability.
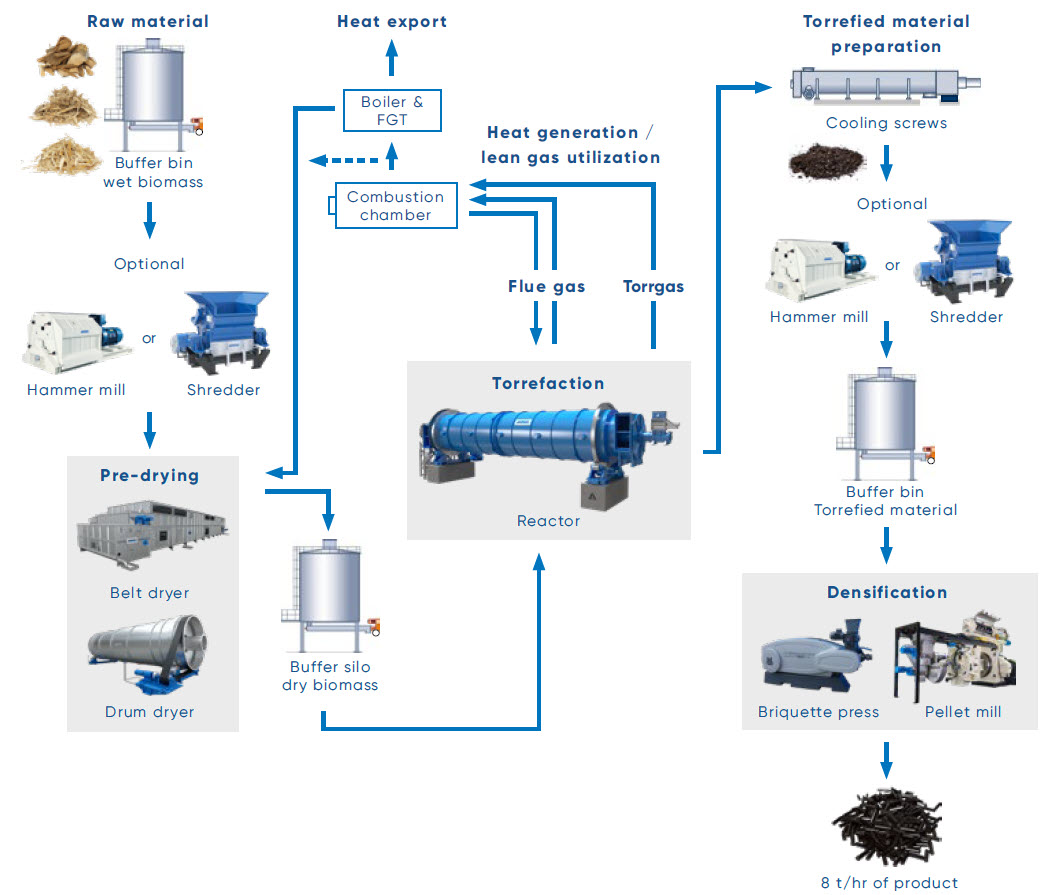
Key Characteristics of Torrefaction
- Lower operating temperatures
- Single, solid fuel output
- Simpler and more stable operation
- Well-suited for mixed waste streams
Torrefaction is increasingly used in MSW processing, RDF upgrading, and co-firing applications where consistency and reliability are critical.
Pyrolysis vs Torrefaction: Key Differences
| Aspect | Pyrolysis | Torrefaction |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 400–700°C | 250–350°C |
| Feedstock Tolerance | Requires uniform input | Handles mixed biomass & MSW |
| Primary Outputs | Char, oil, gas | Solid torrefied fuel, bio-oil, syngas |
| System Complexity | High | Moderate |
| Energy demand | High | Moderate |
| MSW suitability | Limited without extensive sorting | High for combustible fractions |
This comparison highlights why torrefaction is often more practical for real-world waste streams, especially MSW.
Why Torrefaction Is Preferable for Biomass and MSW
Better Handling of Mixed MSW
MSW is inherently heterogeneous. Torrefaction is more forgiving of feedstock variations, making it suitable for refuse-derived fuel (RDF) and other combustible waste fractions. Pyrolysis, in contrast, struggles with inconsistent input without complex pre-processing.
Focused Solid Fuel Production
Torrefaction produces a single, uniform solid fuel, which simplifies storage, transport, and end use. This fuel can be used as a coal substitute in power plants, cement kilns, and industrial boilers.
Lower Energy and Operating Costs
Because torrefaction operates at lower temperatures, it:
- Consumes less energy
- Requires simpler reactor systems
- Reduces operational risk
This makes torrefaction more cost-effective for large-scale MSW and biomass processing.
Easier Integration into Existing Infrastructure
Torrefied fuel behaves similarly to coal, allowing it to be:
- Stored outdoors
- Ground easily
- Fed into existing combustion systems
This is a major advantage for industries looking to adopt waste-derived fuels without major plant modifications.
When Pyrolysis Makes Sense
Pyrolysis can be suitable when:
- The target products include bio-oil or syngas
- Feedstock quality is tightly controlled
- Chemical recovery is a priority
However, for municipal and industrial waste management, these conditions are often difficult to achieve consistently.
Torrefaction as a Practical Waste Solution
Both pyrolysis and torrefaction have roles in thermal waste treatment. Pyrolysis offers flexibility through multiple outputs but comes with higher complexity and cost—particularly when applied to MSW.
Torrefaction stands out as a simpler, more robust, and scalable technology for processing both biomass and municipal solid waste. By producing a stable, high-energy solid fuel and tolerating feedstock variability, torrefaction aligns well with modern waste-to-energy, RDF upgrading, and sustainable fuel production goals.
As industries and municipalities seek reliable ways to convert waste into value, torrefaction continues to gain importance as a practical and efficient thermal treatment technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Torrefaction is generally better when the goal is to produce a stable solid fuel from biomass or MSW. It is simpler to operate, consumes less energy, and produces a uniform fuel that is easier to store, transport, and use in existing industrial systems
Yes, torrefaction can process the combustible fraction of municipal solid waste, including RDF. It improves fuel quality, reduces moisture, and produces a solid fuel suitable for co-firing and industrial applications
Yes, torrefaction is well-suited for mixed biomass and MSW streams. It is more tolerant of feedstock variation compared to pyrolysis, which typically requires uniform and well-sorted input material
Torrefied fuel resembles coal because torrefaction removes moisture and light volatiles, increasing carbon concentration. This results in higher energy density, improved grindability, and hydrophobic behavior similar to coal
Yes, torrefied biomass and torrefied MSW fuel can be used in power plants for co-firing with coal. It is compatible with existing fuel handling systems and helps reduce fossil fuel consumption
Torrefaction is gaining popularity because it offers a practical way to convert biomass and MSW into a high-quality solid fuel with lower energy input, simpler operation, and easier integration into existing infrastructure.



